Classification of proteins on the basis of function
On the basis of their functions the proteins can be classified as following;
I. Homeostatic Proteins
These are soluble proteins that stabilize the pH wherever they occur.

II. Structural Proteins
These are insoluble proteins that take part in formation of structures such as tendon, skin and hair.
III. Hormonal Proteins
Peptide hormones such as Insulin and glicagon help regulation of Glucose metabolism.
IV. Enzymic Proteins
Enzymes are large, complex globular proteins that act as catalysts, e.g., respiratory enzymes, enzymes of Calvin cycle and digestive enzymes.
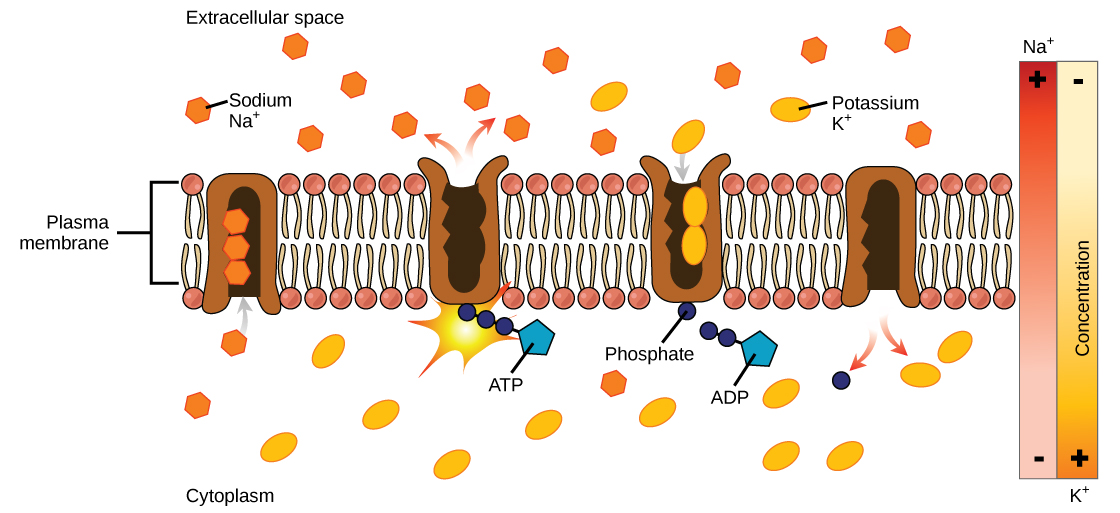
V. Transport Proteins
The proteins involved in transport of metabolites and ions across the membrane, e.g., cell membrane protein and protein of membranes of cell organelles. Another common transport proteins is haemoglobin involved in transport of oxygen in animals.
VI. Contractile Proteins
The proteins concerned with movements are contractile proteins. e.g., those present spindle microtubules, and muscle cells of animals.
VII. Storage Proteins
The proteins that serve the purpose of storage, e.g., aleurone proteins in seeds and casein in milk.
VIII. Protection
Certain proteins provide protection, e.g., antibodies that react with foreign proteins and some other molecules, and fibrinogen and thrombin responsible for blood clotting mechanism.

Comments
Post a Comment